Embedded Finance and Banking As a Service (BaaS): Which One To Choose?
The introduction of technologically advanced systems and integrations bridged several industries together and lowered the entry barriers for almost every market.
Nowadays, more brokerage companies are joining, more digital banks are coming into existence, and more service providers are available for any business you have.
Thus, the BFSI umbrella (Banking, financial services and insurance) is expanding, and more entities are entering the market. For example, non-financial companies can now offer banking services to their customers thanks to embedded finance and BaaS applications.
As a customer or a business owner, you must have stumbled on these two concepts, and we will simplify them for you to understand how you can use them for your company.
Key Takeaways
- Embedded finance is directly integrating a financial services provider into a website or application as a part of the website’s UI.
- Banking as a service uses API integrations to exchange data with a financial institution to provide banking services without redirecting the user to the bank’s website.
- Embedded finance and banking as a service have expanded the FinTech umbrella to include more industries and businesses.
- Baas uses the bank’s technological backend to offer services, while embedded finance offers solutions on the site’s front end.
Understanding Banking As A Service
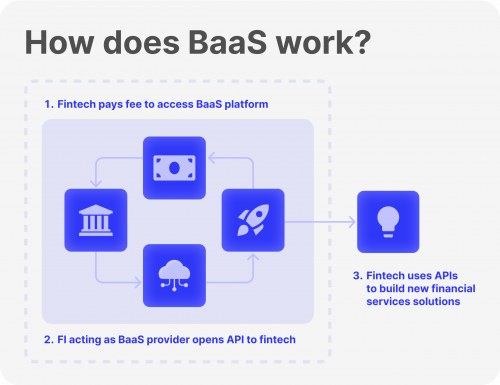
Banking as a service is software that provides non-banking companies with access to financial services for their customers. This way, a website or an application can provide financial solutions to its users without sending them to a third-party site or to the bank’s webpage.
This introduction allows more FinTech companies to emerge, offering a wide range of banking-like services. This method uses white-label solutions to provide FinTech BaaS companies with technical and software means of delivery.
Companies would require more time to develop their BaaS financial solution. Therefore, they purchase a customised platform from providers utilising their experience and knowledge to build similar services.
White label systems are basically ready-to-use platforms that companies configure according to their preferences and the services they provide, besides branding it with their name and logo before launching the product.
Use Cases and Examples
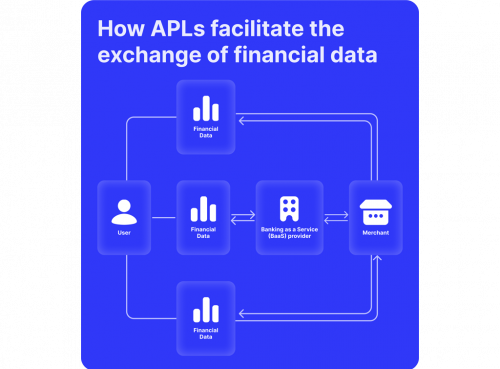
Banking as a service uses different APIs to connect users with services like applying for loans, checking their bank account, and accessing their credit score directly on the FinTech company website/app.
This way, when a user logs into the website, they can interact with their bank and account details, powered by API requests that transmit information and data exchange between the two consoles.
Apple Cards and Revolut use banking as a service to allow their customers to conduct different financial operations online.
Fast Fact
As of March 2023, there are more than 26,000 FinTech companies worldwide, with over 11,000 startups operating in the United States.
Understanding Embedded Banking
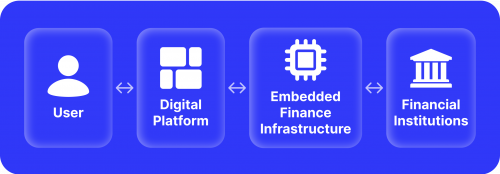
Embedded banking has been used for a long time now, especially in online shops and digital stores. It means integrating the financial service provider (banks) in streamlining a non-financial service provider.
Reports say that 60% of the UK’s adult population – or 3 in 5 adults – use embedded services online on various websites.
This way, users can clearly see they are requesting a financial service provided by their bank, for example. This enables companies of all kinds to connect their customers with their banking infrastructure to execute certain functions like paying, confirming a transaction or approving access to funds.
Use Cases and Examples
Embedded services are present in almost every online store on the checkout page; when customers pay for their shopping cart online, they can see they are paying using their bank account.
This approach is more commonly used than BaaS and is becoming more popular with the advancements of FinTech companies and services. E-wallets and digital banks play a major role in driving embedded finance growth worldwide.
For example, when you add a payment method to Amazon or on the checkout page of your automobile dealership, you are inserting your credit card information and being redirected to the bank’s page to finalise the payment.
Comparing Embedded Finance and BaaS
Banking as a service and embedded finance serve similar functions as they interact with the user’s financial institutions or banks. However, there are distinct differences between embedded finance and BaaS that you must consider.
Access to Financial Services
You can look at the difference between them as backend and frontend. BaaS systems provide a back-end integration with banks, using the provider’s technological foundation to deliver financial solutions.
On the other hand, embedded finance is present on the front end of the FinTech company’s website or application, and the user can clearly find or choose their bank while conducting the requested transaction.
Moreover, the difference between them lies in the financial services each model targets. For instance, BaaS offers a wider range of tools to interact with the bank account, while embedded finance is integrated to enable the user to execute a specific operation, like paying.
Solving Customer’s Problems
Each model has a different objective. BaaS platforms use neatly designed interfaces and ready-to-use solutions that are customisable. Any company that uses a white label CRM can adjust the system to their preferences and improve it constantly to improve their customer experience in the long term.
However, Embedded finance ensures the customer interface is smooth and functional, integrating financial services in the website’s streamline only to manage specific orders.
Brand Customisation
Banking as a service uses turnkey solutions, meaning that the company can add their branding, logo and name and launch its services. This method is focused on the longer-term impact on customer’s experience and associations.
On the other hand, embedded finance is focused on the sole execution of a certain financial operation. Therefore, embedded finance has minimum branding because it strives to streamline financial services for a specific function.
The Future of Embedded Finance and Baas
Embedded finance and banking as a service are innovative ways to offer financial services directly and indirectly, aiming to serve customers and connect them with their financial institutions differently.
Nowadays, you can find a plethora of providers that deliver financial services online using centralised and decentralised economies, and bandwidth is only expected to keep growing.
Embedded finance is expected to reach an overall transaction value of $7 trillion by 2026, with a revenue potential of over $50 billion. These figures justify the boom in embedded finance and banking-as-a-service firms that emerge daily.
On the other hand, banking as a service recorded $11 billion in revenue in 2022, which is expected to increase three-fold by 2027.
Which One Shall You Choose For Your Company?
There is much to expect from BaaS and embedded finance, and the choice depends on your company and the type of business you are providing.
If you run an online store or you sell non-financial products and services, and you want to include a one-click purchase or scan and buy functions, then you must follow the embedded finance. This model allows you to offer financial services like quick checkouts and redirection to the bank checkout page.
However, suppose you own a service-based business and want to integrate with the banking infrastructure or financial institution to provide broader financial services. In that case, banking as a service model fits you better.
This way, you connect your clients with their financial service provider without having your own banking infrastructure.
Conclusion
Embedded finance and banking as a service are two different methods to offer financial services to non-licensed financial institutions and through API integrations with financial service providers.
These two concepts smoothen the user experience while interacting with non-financial businesses and websites, especially those requiring purchasing or ordering a product/service.
BaaS and embedded finance broadened the FinTech sector to include businesses of all types, providing innovative solutions that found their way to the futurist Web 3.0 applications.


